TL;DR
Arrays are data types that holds collections of data, saved side by side or contiguously in memory. They are fast at reading and
writing values with a time complexity of O(1).
PROS
- Compact Code; Store lots of objects in a single array without having to define multiple variables
- Memory Efficient; Since the elements in an array are saved side by side, no extra/wasteful memory is allocated
- Fast; With a time complexity of
O(1), reading and writing values to arrays is blazing fast even when reading randomly
CONS
- The size of an array is fixed. Therefore, adding extra items to the array is not as fast and efficient as simple reads/writes
- Due to the fact that arrays store information in contiguous memory locations, deletion and insertion procedures are exceedingly difficult to implement.
What Are Arrays?
Arrays, (also known as Static Arrays) are one of the most popular data types across several programming languages. What makes them stand out is the speed
at which data is read from or written to the array (with the Big O notation of constant time, O(1), if you are into that kinda
thing, 🙃).
It accomplishes this level of speed by literally saving the values of the array side by side in memory… Which is the reason why you’d have to declare the size of the array when creating the array.
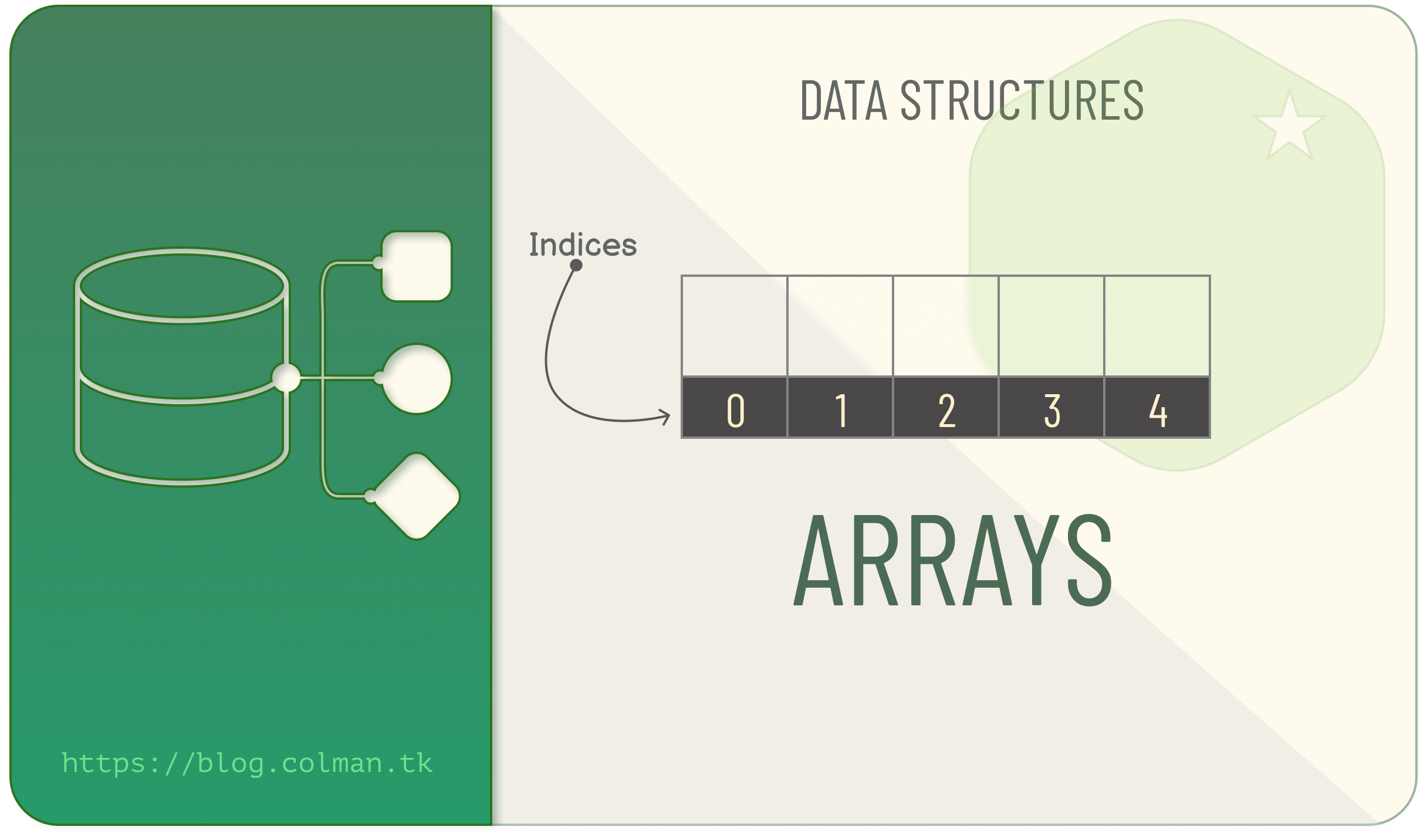
To illustrate how data writing and retrieval from arrays, lets consider the following; We create an array, X,
with the size of 5 and the compiler decides to provision a block of memory starting from 0x00 to 0x04…
If we wanted to get the third item in the array, we simply tell the program to get that element by calling X[2],
(in most languages, arrays are Zero Based, i.e, the first element is 0, the second is 1 …) the program then checks
the memory for the third item (by simply counting 3 from the start of the array (0x00), which would be 0x02).
Though Arrays have super high read/write speed, they, by definition, have a fixed length. Therefore, they do not allow adding additional items. An array of length 5, can only store 5 items, not more.
Most times however, we do not know the size if an array initially and have to determine that during runtime. For this, Dynamic Arrays were created.
Dynamic Arrays
Dynamic Arrays work the same way as Static Arrays do but with the ability to grow and shrink when needed. They however are not as efficient when it comes to adding extra items to the array. Say we have an array with the length of 5, if we wanted to add another item to the array, effectively making it an array of 6 items, The program has to;
- Create a new array with the size of 6 elements,
- Copy the previous array into the new array,
- Add the new data to the array.
Though Dynamic Arrays still maintain the read/write speed of Static Arrays and also have the ability to grow, growing
them is not as efficient (with the Big O notation of O(n)).
Thank You 🥳.
Suggestions and Corrections are very welcome, Please comment below